SENSORS
Electrical Automation Sensors are sensors that can measure the electrical current, voltage, power and other electrical properties of a device. They are using to monitor things like temperature, humidity, light intensity, vibration, pressure, liquid level, motion, smoke/gas detection, and more. There are two types of Electrical Automation Sensors: analog and digital. Analog Sensors use a variable resistor to control the amount of electricity passing through them. These are typically less expensive than their digital counterparts, but cannot have multiple simultaneous reads. Digital Sensors can take multiple readings at the same time, which means they can provide real-time data. This makes them great for measuring things like temperature, humidity, and light intensity. Power meters; circuit breakers; demand controllers; Relay contacts; and Contactors (contactor). These devices are used to monitor and limit the amount of electricity that can pass through an electrical circuit. They are typically installed at the point of use and measure the current flowing through the building wiring. Electrical automation sensors are used in residential, commercial, industrial, education, healthcare and government applications.
DCZ Electric as limit switch, inductor sensor, capacitive sensor, photocell, flow measurement sensors, field sensors, industrial imaging sensors, encoder, gas analyzers, light curtain, contrast sensors, distance measurement sensors, magnetic cylinder sensors, motor- We wholesale and export Turkish made sensors such as feedback systems, optoelectronics safety devices, automatic identification sensors, brightness sensors, dust measuring devices and fork sensors.
Limit Sensors
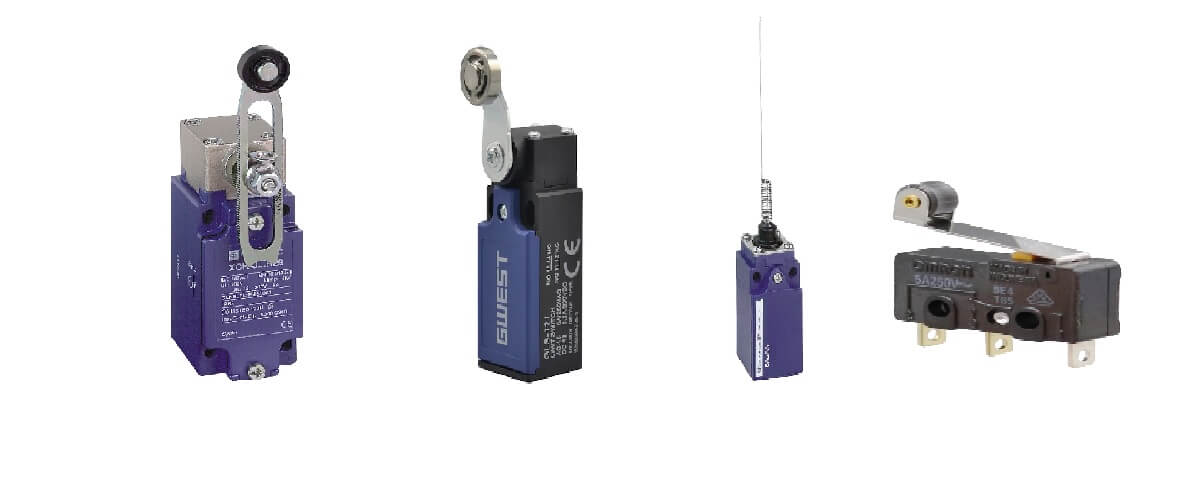

Limit switches are used to regulate the flow of electric current through a circuit. They are typically used in conjunction with other components (such as relays) to provide precise control over the amount of power flowing through a circuit. Limit switches can be mechanical or electronic. Mechanical limit switches consist of two contacts separated by a spring mechanism. When the load exceeds the set point, the spring comes down and closes the contacts. Electronic limit switches use solid-state electronics to detect an overload condition and then automatically open the contacts.
Inductive sensors
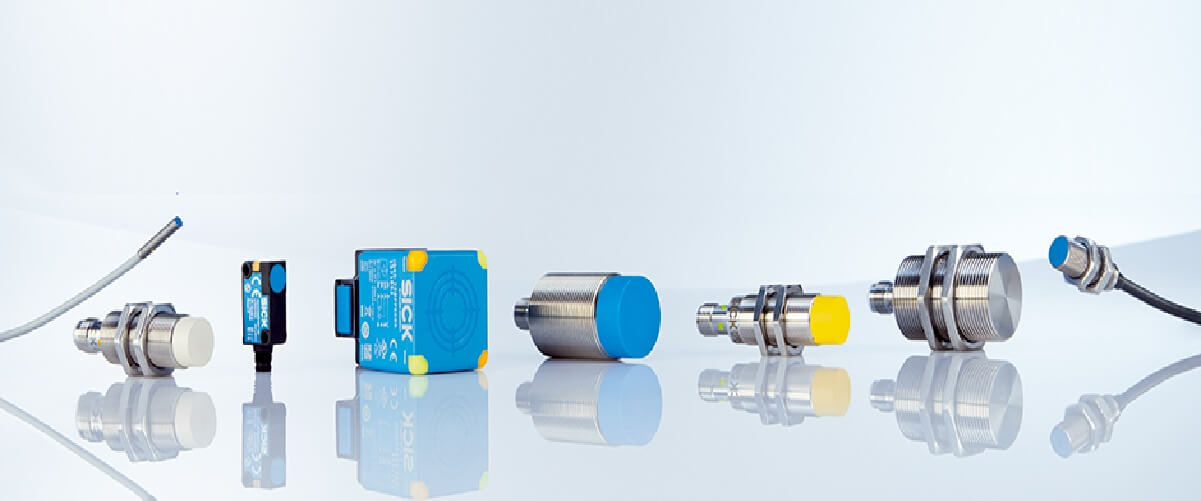

Inductive sensors are used to measure the electrical properties of materials. These sensors consist of two electrodes placed at different points on the material being measured. When current flows through the material between these two electrodes, the sensor detects this flow and measures its density. This can then be translated into other information about the material.
The inductive sensor works by measuring changes in magnetic flux density (a change in electric current). This results in a change in voltage across the electrode. A coil around the sensor creates a changing magnetic field. As the material moves in the magnetic field, eddy currents are induced in the material. Eddy currents create their own magnetic field, which is opposite to the original field. The resulting change in flux causes a change in voltage across the electrodes. By measuring the voltage, we can determine how much current flows through the material.
Capacitive Sensor
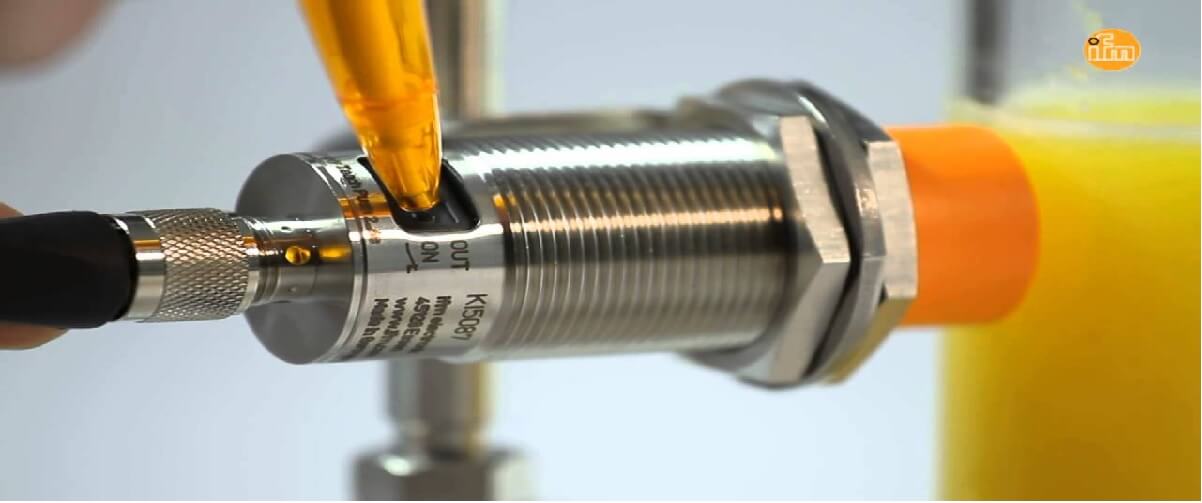

Capacitive sensors measure electric field changes from the proximity of an object. This occurs when an object approaches or moves away from the sensor. They are based on the principle that any change in electrical properties (capacitance) affects the flow of electrons. As this happens, the potential difference between two points on the surface of the sensing element changes. This change can be electronically measured and converted to an output voltage. Capacitive sensors are used in many applications, including touchscreens, gas sensing, proximity switches, motion sensors, and other types of sensors.
Photocell Sensor
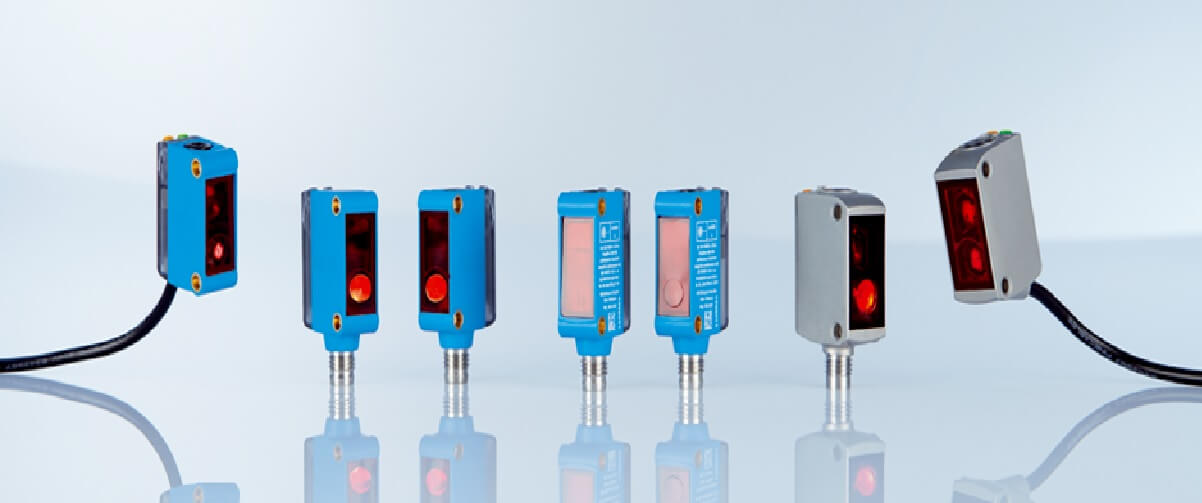

The photocell sensor is essentially a light dependent resistor (LDR). LDRs are used in many applications, from motion detectors to smoke alarms. They consist of two parallel conductors separated by a semiconductor material that conducts electricity only when exposed to light. In the absence of light, the semiconductor material becomes devoid of electrons and creates an electric field between the conductors. This field creates a voltage difference that can be measured later.
The electric photocell sensor must be exposed to light in order to work. At runtime, the circuit measures the amount of current flowing through the sensor, which shows how much light hits the device. If the sensor is not exposed to any light, the circuit will measure zero current. When the sensor detects enough light, the circuit will start to produce a small current that increases until the light reaches its maximum brightness. At this point the circuit stops measuring the current and starts measuring the voltage drop across the sensor. The amount of light hitting the sensor determines the voltage drop in the sensor.
Flow Measurement Sensors

Flow sensors are used to measure flow rates through pipes and other ducts. Flow sensors can be divided into two types, magnetic and ultrasonic.
Magnetic flow sensors use magnetism to detect changes in fluid flow. When the fluid passes a coil, eddy currents are induced in the metal wire coils. These eddy currents produce their own magnetic field, which can be detected by a Hall effect probe mounted perpendicular to the direction of flow. This distance between the probe and the coil is called the gap.
Ultrasonic flow sensors use sound waves to detect changes in fluid velocity. Ultrasonic flow sensors work by transmitting high-frequency acoustic signals down the pipe wall. When these signals are reflected from any object inside the pipe, they return to the transducer at different times depending on their position relative to the transducer. By measuring this time difference, the velocity of the fluid can be calculated.
Field Sensor
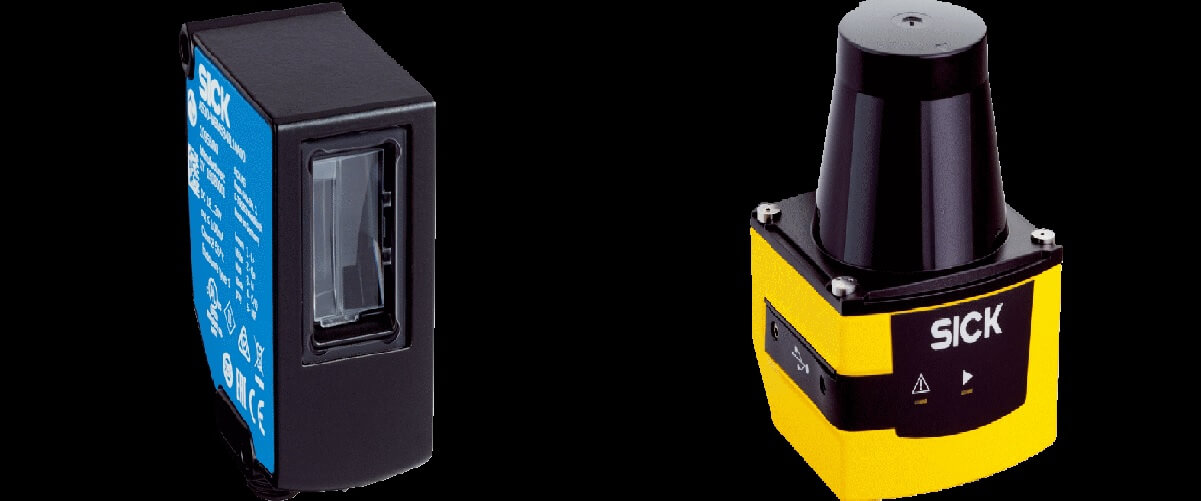

A field sensor is a device that measures the electrical potential difference between two points. Field sensors consist of two electrodes, one positive and one negative, at each measured point. Each electrode has a voltage reading attached to it. When a current flows through the first electrode, it creates a small electric field around it. This field then travels through space until it reaches the second electrode. When the field reaches the second electrode, the voltage drop between the two electrodes is recorded. The voltage difference between the two points represents the amount of charge carried by the current passing through the first electrode.
Electric field sensors are commonly used to detect certain ion levels in water, but have also been applied in other fields, including medical diagnostics and environmental monitoring.
Industrial Viewing Sensors
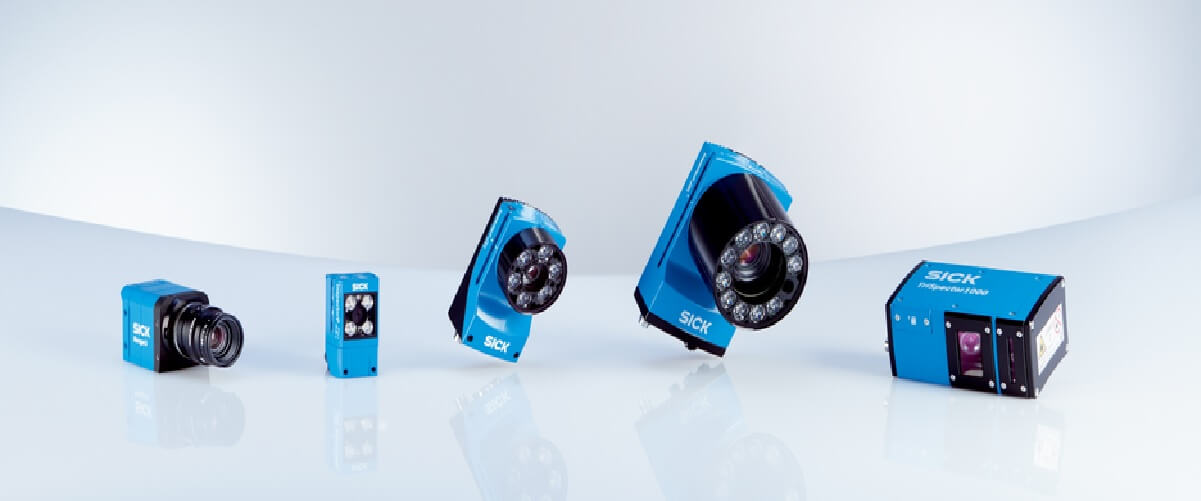

Viewing sensors are semiconductor devices that can convert optical images into electrical signals. They are used in cameras, video recorders, telescopes, security systems, medical devices, and many other applications where they need to capture light and convert it into an electronic signal. Industrial image sensor, on the other hand, is the use of image sensor in industrial automation, factory automation, machine vision, robotics, automotive, aerospace, etc. refers to its application in the fields.
Encoder
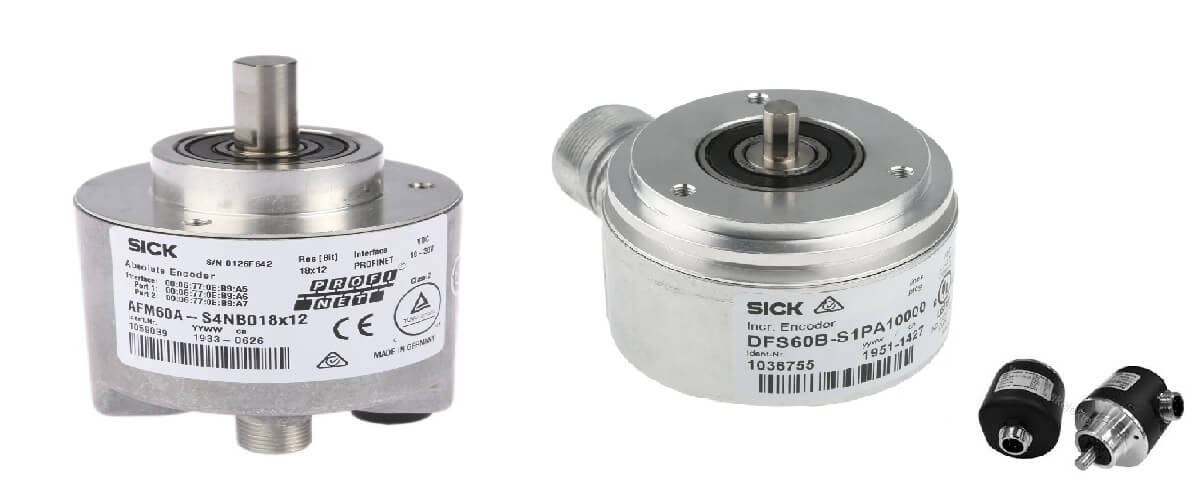

An industrial encoder is a device that converts rotational motion into electrical pulses. They are used in machine tools, robots, vehicles and machinery. This type of encoder consists of a disk called a rotor that rotates at high speed while attached to a shaft. As the shaft rotates, the disk passes by the read heads, which send out pulses. These pulses can then be converted to digital signals.
Gas Analyzers
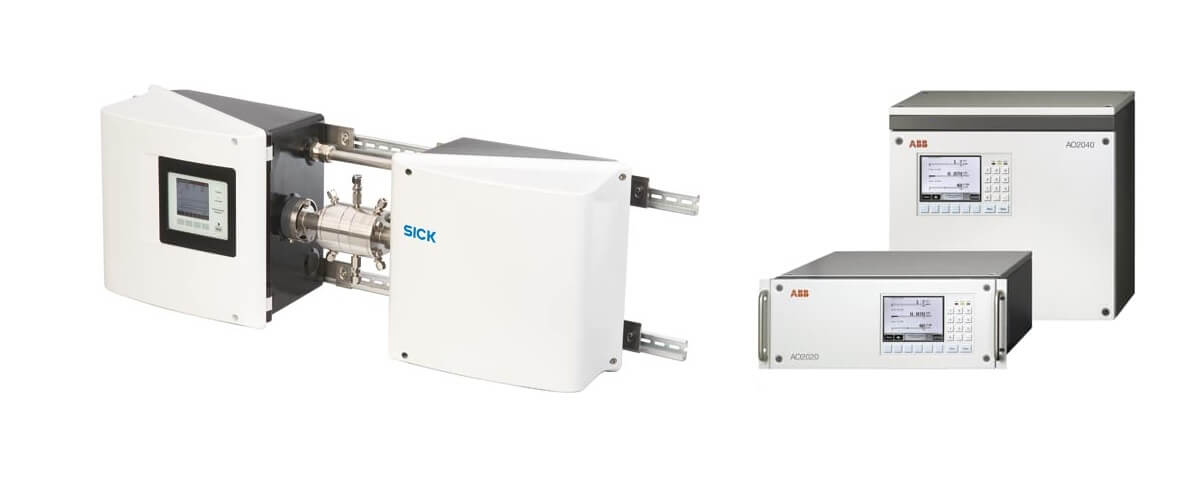

An industrial gas analyzer is used to measure gases and vapors at high temperatures and pressures. They are used in chemical processes, power generation and refinery industries. They are also used in semiconductor manufacturing, food processing, pharmaceuticals and other industries where purity is critical.
Gas analyzers work by measuring changes in electrical conductivity or optical properties that occur when certain gases come into contact with materials in the sensor chamber. This change causes a later measurable shift in the physical properties of the material. There are two types of sensors, those that use thermal conductivity and those that use optical absorption.
Thermal conductivity sensors work based on how well heat is transmitted through a substance. When a sample of gas comes into contact with the tube of a sensor, heat flows from the hot side to the cold side. The time required for this transfer is proportional to the concentration of the gas being analyzed. The thermal conductivity sensor measures the difference between the temperature of the hot side and the cold side of the sensor.
Optical absorption sensors work according to the Beer-Lambert law. As light passes through a substance, some wavelengths are absorbed while others pass through. By shining a light on a sample and measuring the intensity of the reflected light, the concentration of the gas can be determined.
Light Curtain
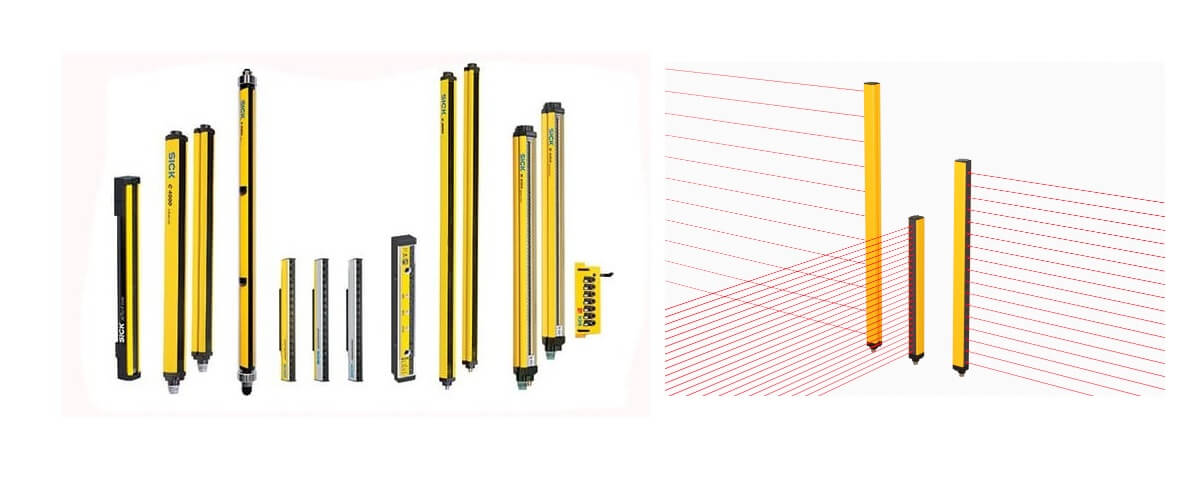
Industrial light curtain sensor is a kind of photodiode that can detect the position of objects within the field of view. This technology uses infrared radiation to determine the distance from the object. Industrial light curtains are used in many different industries, including manufacturing, material handling, automotive, packaging, food processing and pharmaceuticals.
Distance Measurement Sensors
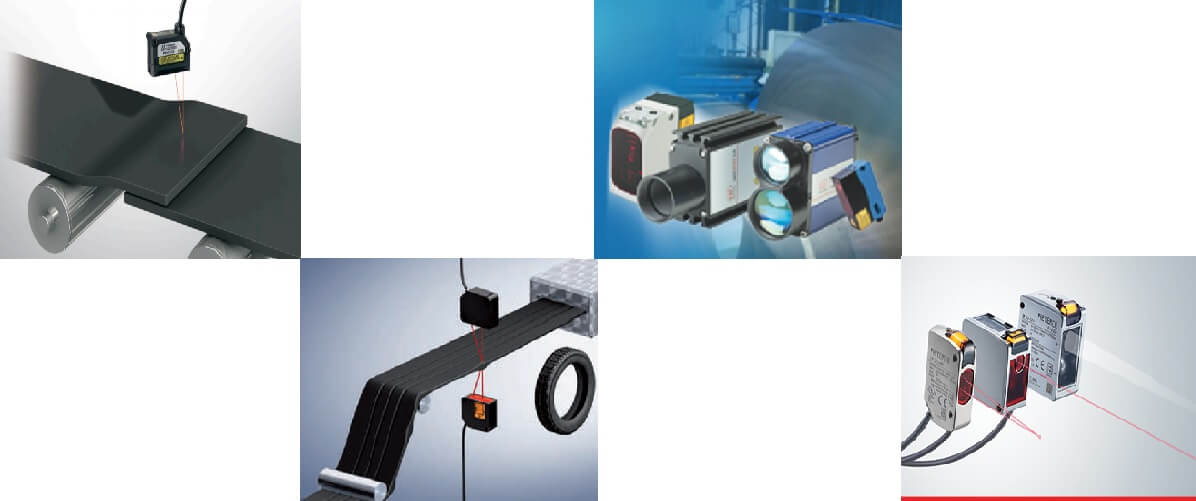

The distance measuring sensor is a kind of non-contact optical distance measuring tool that can determine the distance between two objects without the need to touch them. Triangulation technique is used to operate this device. In other words, this sensor uses three light sources to determine the distance between a reference point and a target object. These three light sources are directed to the target and returned to the receiver. The distance between the target and the receiver can be determined using the time period of the reflected signal.
Magnetic Cylinder Sensor

A magnetic cylinder sensor is a device that detects changes in current flowing through a conductor using electromagnetic induction technology. Magnetic field sensors are often used to measure the speed and direction of rotating machinery, and they can also be used to trigger events related to the rotation of the machine. They can also be used to monitor material flow in pipes and other channels.
Engine-Feedback Systems

Engine feedback systems are used to prevent the engine from overheating or burning out. They consist of a sensor that detects temperature changes in the motor and transmits the data to a feedback circuit. The temperature difference is then converted into an electrical output and applied to the motor by this circuit. The feedback system shuts down the engine when the temperature rises above what is considered normal. The motors are controlled by servo controls. They work by monitoring the position of the motor shaft and sending signals to the motor to turn it in the direction of rotation or in the opposite direction, depending on the direction it needs to move.
Optoelectronic Safety Devices
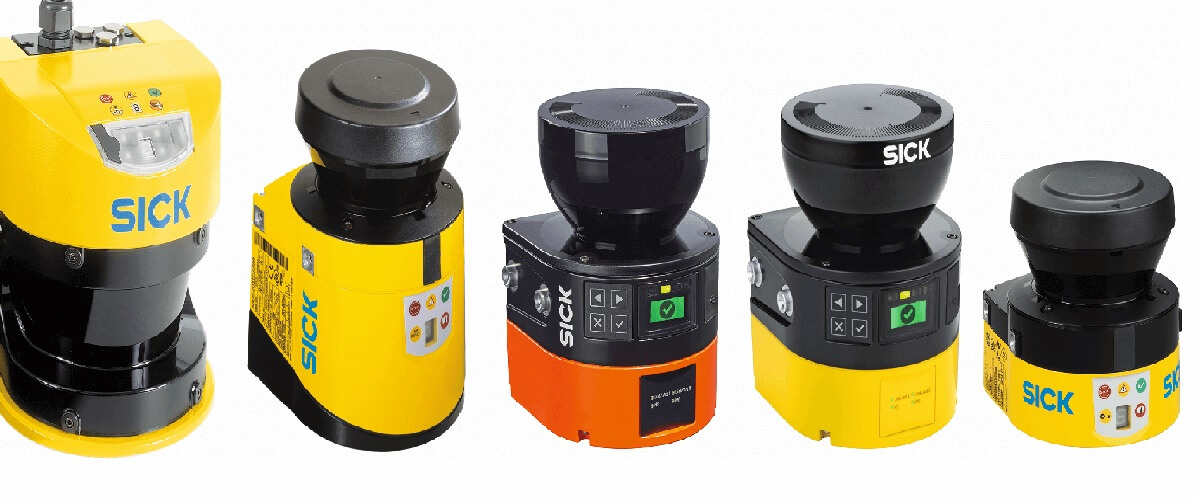

Optoelectronics is used to monitor the movements of any electronic device. They use light waves to detect electrical signals from the controlled device. Optoelectronics devices can be used to warn of dangers that may occur if certain conditions are abnormal. Optoelectronics devices work according to the principle of photoelectric effect in terms of working principle. When light hits a substance, some of its energy is converted into electricity. Using this feature, optoelectronics devices can measure data about their environment. Optoelectronics sensors can be divided into two groups, active and passive. Active optoelectronics devices emit light to determine the amount of light reflected back to them. Passive optoelectronics devices do not produce light, but instead rely on the reflection of light from other sources.
Automatic identification systems are industrially divided into 3 basic types. Barcodes are a type of two-dimensional (2D) matrix that can hold data about a particular item. They are widely used in a variety of businesses, including retail, shipping, inventory control, and others. A barcode consists of a series of black bars and white spaces arranged in rows and columns. Each column represents a separate character, while each row represents a combination of characters. 2D code is a type of symbology that uses a square grid of 1s and 0s to represent information. Radio frequency identification is a wireless method of automatically identifying objects using radio waves. RFID tags are small tags that store unique identifiers and have antennas to transmit data wirelessly.
Brightness Sensors

Luster Sensors are used to detect both visible and invisible marks that glow under ultraviolet (UV) light. These sensors can detect all kinds of signs, including those invisible to the naked eye. They are widely used in industries such as automotive manufacturing, packaging, printing and pharmaceuticals.
Dust Measuring Devices

The PCE-MPC20 is a dust measuring instrument that can measure both PM10 (particles smaller than 10 microns) and PM2.5 (particles less than 2.5 microns). This device is used to monitor particulate matter emissions from combustion sources and other industrial processes. Dust measurement systems are widely used for air quality monitoring and control. They are often used for continuous measurements and provide operators with real-time data. Dust measurement systems, mining, chemical processing, construction, power generation, etc. It is used in industries where dust emission is critical, such as.
U type Sensor
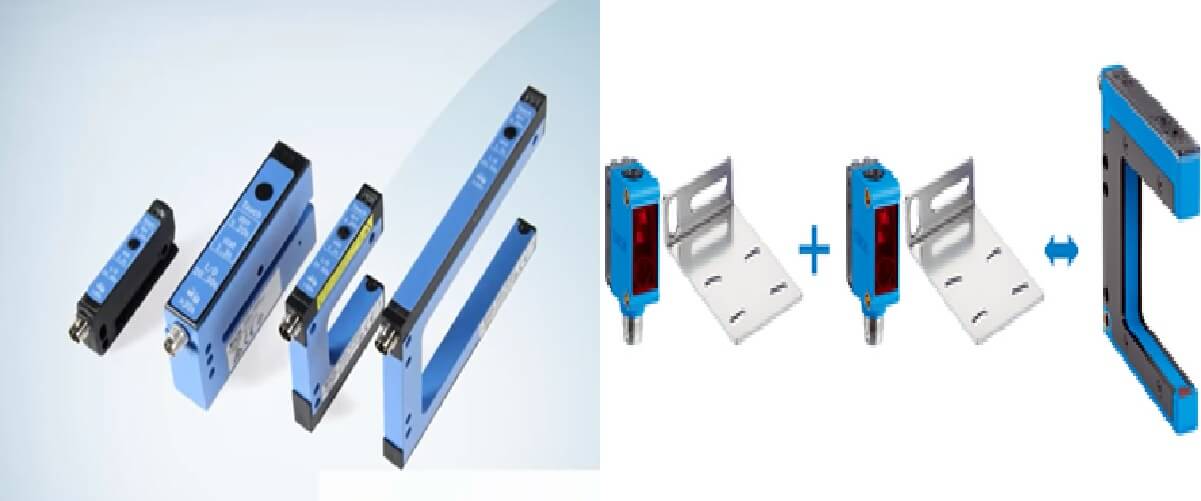

A U sensor is a device that detects if something is passing between its two arms and sends a signal when it does.
